|
Gaudi Framework, version v21r8 |
| Home | Generated: 17 Mar 2010 |
|
Gaudi Framework, version v21r8 |
| Home | Generated: 17 Mar 2010 |
#include <KeyedContainer.h>
Implementation helpers. | |
| container_type | m_cont |
| Map container to facilitate object access by key. | |
| seq_type | m_sequential |
| Array to allow sequential access to the object (can be ordered). | |
| seq_type * | m_random |
| Array to allow random access to objects (not exposed). | |
| FORCE_INLINE value_type | i_object (const key_type &k) const |
| Internal function to access objects within the container. | |
| long | i_erase (const_reference v, const key_type &k) |
| Internal function to erase an object from the container. | |
DataObject virtual function overloads. | |
| The implementation of these methods is required by the DataObject base class and determines the persistent run-time-type information. | |
| virtual const CLID & | clID () const |
| Retrieve class ID. | |
| static const CLID & | classID () |
| Retrieve class ID. | |
Public Types | |
| typedef DATATYPE | contained_type |
| Definition of the contained object type. | |
| typedef MAPPING | container_type |
| Definition of the implementing container type. | |
| typedef std::vector < contained_type * > | seq_type |
| General container specific type definitions. | |
| typedef contained_type::key_type | key_type |
| Definition of the key type: re-use definition of contained type. | |
| typedef seq_type::value_type | value_type |
| Sequential access: definition of type stored in sequential container. | |
| typedef seq_type::reference | reference |
| Sequential access: reference type used in sequential container. | |
| typedef seq_type::const_reference | const_reference |
| Sequential access: const reference type used in sequential container. | |
| typedef seq_type::iterator | iterator |
| Sequential access: iterator type used in sequential container. | |
| typedef seq_type::const_iterator | const_iterator |
| Sequential access: const iterator type used in sequential container. | |
| typedef seq_type::reverse_iterator | reverse_iterator |
| Sequential access: reverse iterator type used in sequential container. | |
| typedef seq_type::const_reverse_iterator | const_reverse_iterator |
| Sequential access: const reverse iterator type used in sequential container. | |
Public Member Functions | |
Constructors/Destructors | |
| KeyedContainer (void) | |
| Standard Constructor. | |
| virtual | ~KeyedContainer () |
| Destructor. | |
NOT FOR GENERAL USE ObjectContainerBase function overloads. | |
The implementation of these methods ensure the behaviour of the class as a type of class ObjectContainerBase. This base class and its behaviour are only used by "generic" object handlers. These classes collaborate with several classes such as the
For this reason, the entry points in this section are reserved for "generic" object handling and should NOT be used in public. | |
| virtual size_type | numberOfObjects () const |
| ObjectContainerBase overload: Number of objects in the container. | |
| virtual long | add (ContainedObject *pObject) |
| ObjectContainerBase overload: Add an object to the container. | |
| virtual long | remove (ContainedObject *pObject) |
| ObjectContainerBase overload: Remove an object from the container. | |
| virtual ContainedObject * | containedObject (long key_value) const |
| ObjectContainerBase overload: Retrieve the object by reference given the long integer representation of the object's key. | |
| virtual long | index (const ContainedObject *p) const |
| ObjectContainerBase overload: Retrieve the full long integer representation of the object's key from the object base class pointer. | |
| virtual size_type | containedObjects (std::vector< ContainedObject * > &v) const |
| Retrieve the full content of the object container. | |
Container related implementation. | |
These methods allow to manipulate the container as a whole and to retrieve information about the internal behaviour of the container. | |
| size_type | size () const |
| Number of objects in the container. | |
| bool | empty () const |
| For consistency with STL: check if container is empty. | |
| void | reserve (size_type value) |
| Reserve place for "value" objects in the container. | |
| void | clear () |
| Clear the entire content and erase the objects from the container. | |
| virtual const std::vector < const ContainedObject * > * | containedObjects () const |
| Retrieve the full content of the object container by reference. | |
| virtual void | configureDirectAccess () |
| Reconfigure direct access to elements (Needed by POOL data loading). | |
Sequential array access to objects using iterators. | |
Sequential object access using iterators is much faster then object access by key. In case all objects of the container should be addressed, use iterators rather than direct object access.
| |
| iterator | begin () |
| Retrieve start iterator. | |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| Retrieve start const iterator. | |
| iterator | end () |
| Retrieve terminating iterator. | |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| Retrieve terminating const iterator. | |
| reverse_iterator | rbegin () |
| reverse_iterator returns the beginning of the reversed container | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rbegin () const |
| const reverse_iterator returns the beginning of the reversed container | |
| reverse_iterator | rend () |
| reverse_iterator pointing to the end of the reversed container | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rend () const |
| const reverse_iterator pointing to the end of the reversed container | |
Random access to objects in the container. | |
Access to objects is given by Key.
Please note, that random object access is nearly in all cases significantly slower than sequential access. If all objects in the contaienr should be addresses sequentially, use iterators rather than direct access. Direct access should only be used for selective retrieval of objects. | |
| value_type | object (const key_type &kval) const |
| Object access by key. | |
| value_type | operator() (const key_type &kval) const |
| STL algorithms support for object access. | |
Insert/Remove objects from the container. | |
Objects generally are identified by key.
Since keys are stored with the objects, insertions and removals are possible by key or by reference. | |
| long | erase (const key_type &kval) |
| Remove/erase object (identified by key) from the container. | |
| long | erase (const value_type val) |
| Remove/erase object (identified by pointer value) from the container. | |
| long | erase (iterator pos) |
| Remove/erase object (identified by iterator) from the container. | |
| void | erase (iterator pos_start, iterator pos_stop, bool use_temp=false) |
| Remove/erase objects by iterator range. | |
| const key_type & | insert (const value_type val, const key_type &kval) |
| Insert entry to the container with a valid key. | |
| const key_type & | insert (const value_type val) |
| Insert entry to the container with automatic key assignment. | |
Private Types | |
| typedef Containers::traits < container_type, contained_type > | traits |
| Traits class definition. | |
Friends | |
| struct | GaudiDict::KeyedContainerDict< DATATYPE > |
Classes | |
| struct | _InsertRelease |
| Internal functor for insertion of objects. More... | |
| struct | _RemoveRelease |
| Internal functor for insertion of objects. More... | |
This class represents a container, where the contained objects are accessed by a key. Such a key can be any class, which is able to convert to and from a 32-bit (long) integer.
To insert objects into the container, this implementation determines the key in the following way:
Access to objects is given two-fold:
The KeyedContainer class uses for further specialization a traits class. By specializing these traits extra behaviour can be forced on request for special containers or special keys.
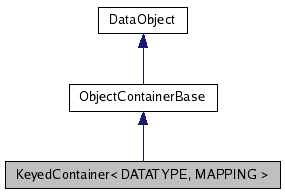
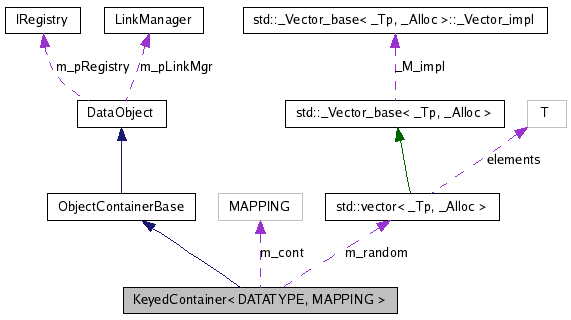
Definition at line 64 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef DATATYPE KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::contained_type |
| typedef MAPPING KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::container_type |
| typedef std::vector<contained_type*> KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::seq_type |
General container specific type definitions.
The following type definitions are generic to most STL containers and are also presented by the KeyedContainer class. These forward declarations typically are used by STL algorithms. Definition of the STL sequential access type
Definition at line 81 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef contained_type::key_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::key_type |
Definition of the key type: re-use definition of contained type.
Definition at line 83 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef seq_type::value_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::value_type |
Sequential access: definition of type stored in sequential container.
Definition at line 85 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef seq_type::reference KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::reference |
Sequential access: reference type used in sequential container.
Definition at line 87 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef seq_type::const_reference KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::const_reference |
Sequential access: const reference type used in sequential container.
Definition at line 89 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef seq_type::iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::iterator |
Sequential access: iterator type used in sequential container.
Definition at line 91 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef seq_type::const_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::const_iterator |
Sequential access: const iterator type used in sequential container.
Definition at line 93 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef seq_type::reverse_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::reverse_iterator |
Sequential access: reverse iterator type used in sequential container.
Definition at line 95 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| typedef seq_type::const_reverse_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::const_reverse_iterator |
Sequential access: const reverse iterator type used in sequential container.
Definition at line 99 of file KeyedContainer.h.
typedef Containers::traits<container_type, contained_type> KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::traits [private] |
Traits class definition.
Specializing traits allows to specialize the container implementation for special needs.
Definition at line 105 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::KeyedContainer | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Standard Constructor.
Definition at line 180 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00181 { 00182 // avoid problems with strict-aliasing rules 00183 seq_type** rptr = &m_random; 00184 seq_type* sptr = &m_sequential; 00185 m_cont.setup((void*)sptr,(void**)rptr); 00186 }
| KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::~KeyedContainer | ( | ) | [inline, virtual] |
| FORCE_INLINE value_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::i_object | ( | const key_type & | k | ) | const [inline, private] |
Internal function to access objects within the container.
Definition at line 133 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00133 { 00134 return 0==m_cont.isDirect() 00135 ? value_type(*(m_random->begin()+traits::hash(k))) 00136 : value_type(m_cont.object(traits::hash(k))); 00137 }
| long KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::i_erase | ( | const_reference | v, | |
| const key_type & | k | |||
| ) | [inline, private] |
Internal function to erase an object from the container.
Definition at line 140 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00140 { 00141 value_type p = value_type(m_cont.erase(traits::hash(k), v)); 00142 if ( p ) { 00143 if ( p->parent() == this ) { 00144 p->setParent(0); 00145 } 00146 } 00147 return traits::release(p) <= 0 ? (long) Containers::OBJ_ERASED 00148 : (long) Containers::OBJ_DELETED; 00149 }
| virtual const CLID& KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::clID | ( | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
Retrieve class ID.
Reimplemented from DataObject.
Definition at line 197 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00197 { return this->classID(); }
| static const CLID& KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::classID | ( | ) | [inline, static] |
Retrieve class ID.
Reimplemented from DataObject.
Definition at line 199 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00199 { 00200 static CLID clid = contained_type::classID() + container_type::classID(); 00201 return clid; 00202 }
| virtual size_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::numberOfObjects | ( | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
ObjectContainerBase overload: Number of objects in the container.
Implements ObjectContainerBase.
Definition at line 222 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00222 { return m_sequential.size(); }
| long KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::add | ( | ContainedObject * | pObject | ) | [inline, virtual] |
ObjectContainerBase overload: Add an object to the container.
Plese see the documentation of the member function
const key_type& insert(DATATYPE* pObject)
for further details.
| pObject | Pointer to the object to be inserted into the container. |
Implements ObjectContainerBase.
Definition at line 602 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00603 { 00604 return traits::identifier(insert(dynamic_cast<typename seq_type::value_type>(pObject))); 00605 }
| long KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::remove | ( | ContainedObject * | pObject | ) | [inline, virtual] |
ObjectContainerBase overload: Remove an object from the container.
Because this function is also called from the destructor of The ContainedObject class, it is no longer possible to deduce the key from the object itself. It is hence necessary to relay on the **NON-EXISTENCE** of virtual inheritance, ie. (void*)pObject = (void*)(contained_object). If the virtual object table is still intact, the normal erase is called.
| pObject | Pointer to the object to be removed from the container. |
Implements ObjectContainerBase.
Definition at line 609 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00610 { 00611 contained_type* p1 = dynamic_cast<contained_type*>(p); 00612 if ( p1 ) { // Normal case; object still fully intact 00613 return this->erase(p1); 00614 } 00615 else if ( p ) { 00616 const ObjectContainerBase* par = p->parent(); 00617 // The following should never occur: object is in a funny state, 00618 // Because the parent was explicitly set to NULL in the 00619 // KeyeObject destructor. 00620 // - It cannot be a KeyedObject: It would not have a parent 00621 // - Still the parent is present: We are not in the destructor 00622 // of KeyedObject 00623 if ( par ) { 00624 Containers::invalidContainerOperation(); 00625 } 00626 return m_cont.erase(0, p)==0 ? (long) Containers::OBJ_ERASED 00627 : (long) Containers::OBJ_NOT_FOUND; 00628 } 00629 return (long) Containers::OBJ_NOT_FOUND; 00630 }
| virtual ContainedObject* KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::containedObject | ( | long | key_value | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
ObjectContainerBase overload: Retrieve the object by reference given the long integer representation of the object's key.
Implements ObjectContainerBase.
Definition at line 253 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00253 { 00254 return i_object( traits::makeKey( key_value ) ); 00255 }
| long KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::index | ( | const ContainedObject * | p | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
ObjectContainerBase overload: Retrieve the full long integer representation of the object's key from the object base class pointer.
Implements ObjectContainerBase.
Definition at line 577 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00578 { 00579 const contained_type* ptr = dynamic_cast<const contained_type*>(p); 00580 if ( ptr ) return traits::identifier(ptr->key()); 00581 return -1; 00582 }
| KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::size_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::containedObjects | ( | std::vector< ContainedObject * > & | v | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
Retrieve the full content of the object container.
| v | Vector of contained objects, which will host all objects contained in this container. |
Definition at line 587 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00588 { 00589 typename seq_type::const_iterator i = m_sequential.begin(); 00590 typename seq_type::const_iterator s = m_sequential.end(); 00591 vec.clear(); 00592 vec.reserve(size()); 00593 for ( ; i != s; i++ ) { 00594 ContainedObject* p = const_cast<typename seq_type::value_type>(*i); 00595 vec.push_back(p); 00596 } 00597 return vec.size(); 00598 }
| size_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::size | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Number of objects in the container.
Definition at line 274 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00274 { return m_sequential.size(); }
| bool KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::empty | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
For consistency with STL: check if container is empty.
Definition at line 276 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00276 { return m_sequential.empty(); }
| void KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::reserve | ( | size_type | value | ) | [inline] |
Reserve place for "value" objects in the container.
Definition at line 278 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| void KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::clear | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Clear the entire content and erase the objects from the container.
Definition at line 280 of file KeyedContainer.h.
| const std::vector< const ContainedObject * > * KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::containedObjects | ( | ) | const [inline, virtual] |
Retrieve the full content of the object container by reference.
Returned is the random access container if in sequntial direct access mode. Otherwise the sequential access container is returned
Definition at line 526 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00526 { 00527 return (const std::vector<const ContainedObject*>*) 00528 ((0==m_cont.isDirect()) ? m_random : &m_sequential); 00529 }
| void KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::configureDirectAccess | ( | ) | [inline, virtual] |
Reconfigure direct access to elements (Needed by POOL data loading).
Definition at line 496 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00497 { 00498 int count = 0; 00499 m_cont.clearDirect(); 00500 typename seq_type::iterator i = m_sequential.begin(); 00501 typename seq_type::iterator s = m_sequential.end(); 00502 for ( ; i != s; i++ ) { 00503 typename seq_type::value_type v = *i; 00504 if ( v ) { 00505 if ( !v->hasKey() ) { 00506 traits::setKey(v, v->key()); 00507 traits::addRef(v); 00508 } 00509 long k0 = traits::hash(v->key()); 00510 if(m_cont.insertDirect(this, v, v, k0) == Containers::OBJ_INSERTED) { 00511 } 00512 } 00513 else { 00514 ++count; 00515 } 00516 } 00517 if ( count > 0 ) { 00518 Containers::cannotInsertToContainer(); 00519 } 00520 }
| iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::begin | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Retrieve start iterator.
Definition at line 305 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00305 { return m_sequential.begin(); }
| const_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::begin | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Retrieve start const iterator.
Definition at line 307 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00307 { return m_sequential.begin(); }
| iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::end | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
Retrieve terminating iterator.
Definition at line 309 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00309 { return m_sequential.end(); }
| const_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::end | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Retrieve terminating const iterator.
Definition at line 311 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00311 { return m_sequential.end(); }
| reverse_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::rbegin | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
reverse_iterator returns the beginning of the reversed container
Definition at line 313 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00313 { return m_sequential.rbegin(); }
| const_reverse_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::rbegin | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
const reverse_iterator returns the beginning of the reversed container
Definition at line 315 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00315 { return m_sequential.rbegin(); }
| reverse_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::rend | ( | void | ) | [inline] |
reverse_iterator pointing to the end of the reversed container
Definition at line 317 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00317 { return m_sequential.rend(); }
| const_reverse_iterator KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::rend | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
const reverse_iterator pointing to the end of the reversed container
Definition at line 319 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00319 { return m_sequential.rend(); }
| value_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::object | ( | const key_type & | kval | ) | const [inline] |
Object access by key.
Access contained objects by key.
| kval | Key of the object to be returned. |
Definition at line 339 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00339 { return i_object(kval); }
| value_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::operator() | ( | const key_type & | kval | ) | const [inline] |
STL algorithms support for object access.
Access contained objects by key using the operator(), which is demanded by STL algorithms.
| kval | Key of the object to be returned. |
Definition at line 350 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00350 { return i_object(kval); }
| long KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::erase | ( | const key_type & | kval | ) | [inline] |
Remove/erase object (identified by key) from the container.
| kval | Key to identify the object within the container. |
Definition at line 375 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00375 { return i_erase(0, kval); }
| long KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::erase | ( | const value_type | val | ) | [inline] |
Remove/erase object (identified by pointer value) from the container.
This member function removes an object, which is identified by its reference from the container. No key value is supplied. To identify the object within the container, the key of the object is used as it can be retrieved using the KeyedObject::key() method.
| val | Reference to object to be removed from the container. |
Definition at line 397 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00397 { 00398 return (val) ? i_erase(val, val->key()) : (long) Containers::OBJ_NOT_FOUND; 00399 }
| long KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::erase | ( | iterator | pos | ) | [inline] |
Remove/erase object (identified by iterator) from the container.
This member function removes an object, which is identified by its reference from the container. No key value is supplied. To identify the object within the container, the key of the object is used as it can be retrieved using the KeyedObject::key() method.
| val | Reference to object to be removed from the container. |
Definition at line 421 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00421 { return erase(*pos); }
| void KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::erase | ( | iterator | pos_start, | |
| iterator | pos_stop, | |||
| bool | use_temp = false | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Remove/erase objects by iterator range.
This member function removes all objects, which are within the sequential iterator range [pos_start, pos_stop[.
| pos_start | Starting iterator of the range to be removed. | |
| pos_stop | Starting iterator of the range to be removed. | |
| use_temp | Flag to indicate that a temporary arry should be used. |
Definition at line 634 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00637 { 00638 bool is_start = start_pos == m_sequential.begin(); 00639 bool is_stop = stop_pos == m_sequential.end(); 00640 if ( is_start && is_stop ) { 00641 // Nothing special. Taken care of by Keyed object manager 00642 } 00643 else if ( is_start || is_stop || use_tmp ) { 00644 std::vector<DATATYPE*> tmp(m_sequential.begin(), start_pos); 00645 tmp.insert(tmp.end(), stop_pos, m_sequential.end()); 00646 std::for_each(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), traits::addRef); 00647 this->erase(m_sequential.begin(), m_sequential.end()); 00648 std::for_each(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), _InsertRelease(this)); 00649 return; 00650 } 00651 std::for_each(start_pos, stop_pos, _RemoveRelease(this)); 00652 seq_type *sptr = &m_sequential; // avoid problems with strict-aliasing rules 00653 std::vector<void*>* v = (std::vector<void*>*)sptr; 00654 std::vector<void*>::iterator i1 = 00655 v->begin() + std::distance(m_sequential.begin(), start_pos); 00656 std::vector<void*>::iterator i2 = 00657 v->begin() + std::distance(m_sequential.begin(), stop_pos); 00658 m_cont.erase(i1, i2); 00659 }
| const KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::key_type & KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::insert | ( | const value_type | val, | |
| const key_type & | kval | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Insert entry to the container with a valid key.
This member function inserts an element, which is identified by its reference to the container. The element will be inserted using the specified key. If the object is already keyed, the long representations of the supplied key and the object's key must agree.
The object will not be inserted and an exception will be raised under the following conditions:
| val | Reference to object to be inserted into the container. The object reference may NOT be NULL. | |
| kval | Key to identify the object within the container. |
Definition at line 533 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00535 { 00536 if ( val ) { 00537 long k0 = traits::hash(kval); 00538 if ( !val->hasKey() || (traits::hash(val->key()) == k0) ) { 00539 if(m_cont.insert(this,val,val,k0) == Containers::OBJ_INSERTED) { 00540 if ( !val->hasKey() ) traits::setKey(val, kval); 00541 traits::addRef(val); 00542 return val->key(); 00543 } 00544 } 00545 } 00546 // Cannot insert object...indicate bad object insertion... 00547 Containers::cannotInsertToContainer(); 00548 return val->key(); 00549 }
| const KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::key_type & KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::insert | ( | const value_type | val | ) | [inline] |
Insert entry to the container with automatic key assignment.
This member function inserts an element, which is identified by its reference to the container. No key value is supplied. The key used to insert the object is retrieved from the element itself. In the event the object already has a key, the assigned key of the object is used. If no key was assigned to the object, (i.e. the object's key is equal to the invalid key), a key is generated according to the number of objects present in the container.
The object will not be inserted and an exception will be raised under the following conditions:
| val | Reference to object to be inserted into the container. |
Definition at line 554 of file KeyedContainer.h.
00555 { 00556 if ( 0 != val ) { 00557 if ( val->hasKey() ) { 00558 if (m_cont.insert(this,val,val,traits::hash(val->key())) 00559 == Containers::OBJ_INSERTED) { 00560 traits::addRef(val); 00561 return val->key(); 00562 } 00563 } 00564 long k0; 00565 if ( m_cont.insert(this, val, val, &k0) == Containers::OBJ_INSERTED ) { 00566 traits::setKey(val, traits::makeKey(k0)); 00567 traits::addRef(val); 00568 return val->key(); 00569 } 00570 } 00571 // Cannot insert object...indicate bad object insertion... 00572 Containers::cannotInsertToContainer(); 00573 return val->key(); 00574 }
friend struct GaudiDict::KeyedContainerDict< DATATYPE > [friend] |
Definition at line 66 of file KeyedContainer.h.
container_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::m_cont [private] |
seq_type KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::m_sequential [private] |
Array to allow sequential access to the object (can be ordered).
Definition at line 113 of file KeyedContainer.h.
seq_type* KeyedContainer< DATATYPE, MAPPING >::m_random [private] |
Array to allow random access to objects (not exposed).
Definition at line 115 of file KeyedContainer.h.