|
Gaudi Framework, version v21r9 |
| Home | Generated: 3 May 2010 |
|
Gaudi Framework, version v21r9 |
| Home | Generated: 3 May 2010 |
#include <GaudiPython/PythonScriptingSvc.h>
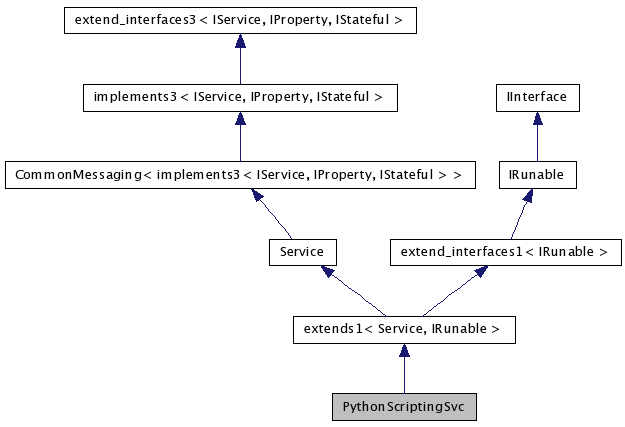

Public Member Functions | |
| PythonScriptingSvc (const std::string &name, ISvcLocator *svc) | |
| Standard Constructor. | |
| virtual StatusCode | initialize () |
| Initialize the service. [IService::initialize()]. | |
| virtual StatusCode | finalize () |
| Finalize the service. [IService::finalize()]. | |
| virtual StatusCode | run () |
| Run the service by taking full control. [IRunable::run()]. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual | ~PythonScriptingSvc () |
| Destructor. | |
Private Attributes | |
| std::string | m_startupScript |
| Startup script. | |
Definition at line 16 of file PythonScriptingSvc.h.
| PythonScriptingSvc::PythonScriptingSvc | ( | const std::string & | name, | |
| ISvcLocator * | svc | |||
| ) |
Standard Constructor.
Definition at line 27 of file PythonScriptingSvc.cpp.
00029 : base_class(name, svc) { 00030 // Declare the startup script Property 00031 declareProperty( "StartupScript", m_startupScript = "" ); 00032 }
| PythonScriptingSvc::~PythonScriptingSvc | ( | ) | [protected, virtual] |
| StatusCode PythonScriptingSvc::initialize | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Initialize the service. [IService::initialize()].
Reimplemented from Service.
Definition at line 39 of file PythonScriptingSvc.cpp.
00041 { 00042 // initialize the Service Base class 00043 StatusCode sc = Service::initialize(); 00044 if ( sc.isFailure() ) return sc; 00045 00046 MsgStream log( msgSvc(), name() ); 00047 00048 // Setup startup script. If none is explicitly specified, then 00049 // use the ApplicationMgr JobOptionsPath property as long as 00050 // the JobOptionsType property is set to "NONE". 00051 if( m_startupScript == "" ) { 00052 SmartIF<IProperty> prpMgr(serviceLocator()); 00053 if ( prpMgr.isValid() ) { 00054 StringProperty tmp; 00055 tmp.assign(prpMgr->getProperty("JobOptionsType")); 00056 if ( tmp.value( ) == "NONE" ) { 00057 tmp.assign(prpMgr->getProperty("JobOptionsPath")); 00058 m_startupScript = tmp; 00059 } 00060 } 00061 } 00062 00063 char* progName[] = { const_cast<char*>("GaudiPython") }; 00064 00065 // Initialize the Python interpreter. Required. 00066 Py_Initialize(); 00067 // Set argv for Tkinter (needs program name) 00068 PySys_SetArgv( 1, progName ); 00069 // Get the Python version 00070 std::string fullversion = Py_GetVersion(); 00071 std::string version( fullversion, 0, fullversion.find_first_of(' ')); 00072 std::string vers(version, 0, version.find_first_of('.',version.find_first_of('.')+1)); 00073 log << MSG::INFO << "Python version: [" << vers << "]" << endmsg; 00074 00075 #if defined(linux) 00076 // This is hack to make global the python symbols 00077 // which are needed by the other python modules 00078 // (eg. readline, math, etc,) libraries. 00079 std::string libname = "libpython" + vers + ".so"; 00080 dlopen(libname.c_str(), RTLD_GLOBAL | RTLD_LAZY); 00081 #endif 00082 00083 00084 // Startup commands 00085 PyRun_SimpleString( "from gaudimodule import *" ); 00086 PyRun_SimpleString( "g = AppMgr()" ); 00087 // backward compatibility with SIPython 00088 PyRun_SimpleString( "theApp = g" ); 00089 PyRun_SimpleString( "def Service(n): return g.service(n)" ); 00090 PyRun_SimpleString( "def Algorithm(n): return g.algorithm(n)" ); 00091 PyRun_SimpleString( "def Property(n): return g.service(n)" ); 00092 // For command-line completion (unix only) 00093 #if !defined( _WIN32 ) 00094 PyRun_SimpleString( "import rlcompleter"); 00095 PyRun_SimpleString( "rlcompleter.readline.parse_and_bind('tab: complete')"); 00096 #endif 00097 return StatusCode::SUCCESS; 00098 }
| StatusCode PythonScriptingSvc::finalize | ( | void | ) | [virtual] |
Finalize the service. [IService::finalize()].
Reimplemented from Service.
Definition at line 101 of file PythonScriptingSvc.cpp.
00103 { 00104 // Finalize this specific service 00105 StatusCode sc = Service::finalize(); 00106 if ( sc.isFailure() ) { 00107 return sc; 00108 } 00109 00110 // Shutdown the Python interpreter 00111 Py_Finalize(); 00112 return StatusCode::SUCCESS; 00113 }
| StatusCode PythonScriptingSvc::run | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Run the service by taking full control. [IRunable::run()].
Implements IRunable.
Definition at line 116 of file PythonScriptingSvc.cpp.
00118 { 00119 MsgStream log( msgSvc(), name() ); 00120 if ( m_startupScript != "" ) { 00121 std::ifstream file(m_startupScript.c_str()); 00122 std::stringstream stream; 00123 if( file ) { 00124 char ch; 00125 while( file.get(ch) ) stream.put(ch); 00126 PyRun_SimpleString( const_cast<char*>(stream.str().c_str()) ); 00127 file.close(); 00128 } 00129 else { 00130 log << MSG::WARNING << "Python startup file " << m_startupScript << " not found" << endmsg; 00131 } 00132 } 00133 PyRun_InteractiveLoop(stdin, "\0"); 00134 return StatusCode::SUCCESS; 00135 }