|
Gaudi Framework, version v23r2 |
| Home | Generated: Thu Jun 28 2012 |
|
Gaudi Framework, version v23r2 |
| Home | Generated: Thu Jun 28 2012 |
#include <Sequencer.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| Sequencer (const std::string &name, ISvcLocator *svcloc) | |
| Constructor(s) | |
| virtual | ~Sequencer () |
| Destructor. | |
| virtual StatusCode | initialize () |
| Initialization of a sequencer. | |
| virtual StatusCode | reinitialize () |
| Sequencer Reinitialization. | |
| virtual StatusCode | start () |
| Sequencer finalization. | |
| virtual StatusCode | execute () |
| The actions to be performed by the sequencer on an event. | |
| virtual StatusCode | stop () |
| Sequencer finalization. | |
| virtual StatusCode | finalize () |
| Sequencer finalization. | |
| virtual StatusCode | beginRun () |
| Sequencer beginRun. | |
| virtual StatusCode | endRun () |
| Sequencer endRun. | |
| void | resetExecuted () |
| Reset the Sequencer executed state for the current event. | |
| virtual bool | branchFilterPassed () const |
| Was the branch filter passed for the last event? | |
| virtual StatusCode | setBranchFilterPassed (bool state) |
| Set the branch filter passed flag for the last event. | |
| virtual bool | isStopOverride () const |
| Has the StopOverride mode been set? | |
| StatusCode | append (Algorithm *pAlgorithm) |
| Append an algorithm to the sequencer. | |
| StatusCode | appendToBranch (Algorithm *pAlgorithm) |
| Append an algorithm to the sequencer branch. | |
| StatusCode | createAndAppend (const std::string &type, const std::string &name, Algorithm *&pAlgorithm) |
| Create a algorithm and append it to the sequencer. | |
| StatusCode | createAndAppendToBranch (const std::string &type, const std::string &name, Algorithm *&pAlgorithm) |
| Create a algorithm and append it to the sequencer branch. | |
| StatusCode | remove (Algorithm *pAlgorithm) |
| Remove the specified algorithm from the sequencer. | |
| StatusCode | remove (const std::string &name) |
| StatusCode | removeFromBranch (Algorithm *pAlgorithm) |
| StatusCode | removeFromBranch (const std::string &name) |
| std::vector< Algorithm * > * | branchAlgorithms () const |
| List of branch algorithms. | |
| StatusCode | decodeMemberNames () |
| Decode Member Name list. | |
| void | membershipHandler (Property &theProp) |
| "Members" property handler | |
| StatusCode | decodeBranchMemberNames () |
| Decode branch member name list. | |
| void | branchMembershipHandler (Property &theProp) |
| "BranchMembers" property handler | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| StatusCode | append (Algorithm *pAlgorithm, std::vector< Algorithm * > *theAlgs) |
| Append an algorithm to the sequencer. | |
| StatusCode | createAndAppend (const std::string &type, const std::string &name, Algorithm *&pAlgorithm, std::vector< Algorithm * > *theAlgs) |
| Create a algorithm and append it to the sequencer. | |
| StatusCode | decodeNames (StringArrayProperty &theNames, std::vector< Algorithm * > *theAlgs, std::vector< bool > &theLogic) |
| Decode algorithm names, creating or appending algorithms as appropriate. | |
| StatusCode | execute (std::vector< Algorithm * > *theAlgs, std::vector< bool > &theLogic, Algorithm *&lastAlgorithm, unsigned int first=0) |
| Execute the members in the specified list. | |
| StatusCode | executeMember (Algorithm *theAlgorithm) |
| Execute member algorithm. | |
| StatusCode | remove (const std::string &algname, std::vector< Algorithm * > *theAlgs) |
| Remove the specified algorithm from the sequencer. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| Sequencer (const Sequencer &a) | |
| Private Copy constructor: NO COPY ALLOWED. | |
| Sequencer & | operator= (const Sequencer &rhs) |
| Private assignment operator: NO ASSIGNMENT ALLOWED. | |
Private Attributes | |
| StringArrayProperty | m_names |
| std::vector< bool > | m_isInverted |
| StringArrayProperty | m_branchNames |
| std::vector< Algorithm * > * | m_branchAlgs |
| std::vector< bool > | m_isBranchInverted |
| BooleanProperty | m_stopOverride |
| bool | m_branchFilterPassed |
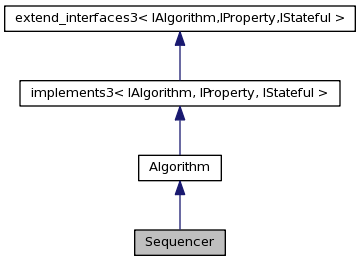
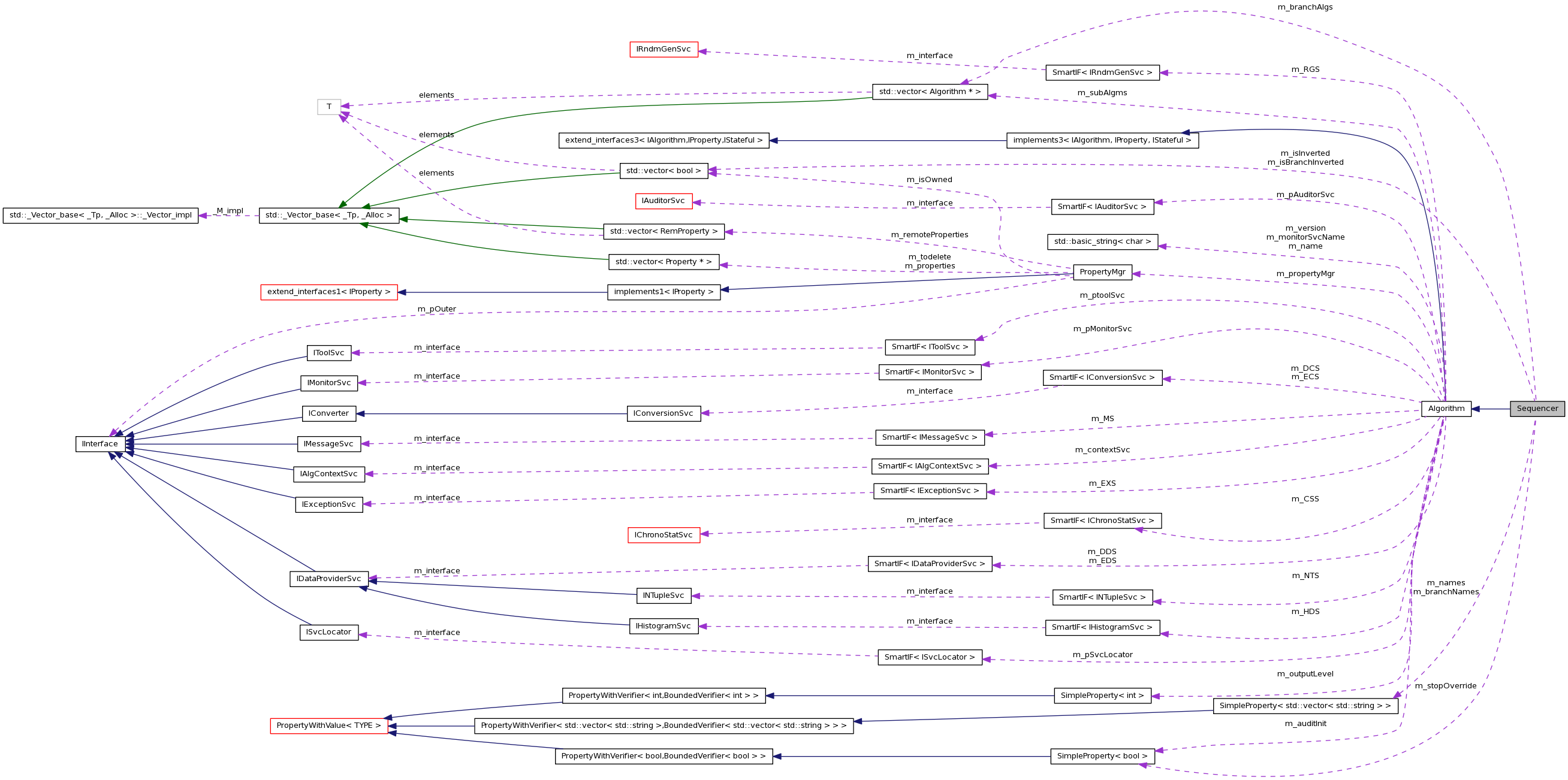
ClassName: Sequencer.
Description: A Sequencer is essentially a list of Algorithms and is responsible for their management. Note that Sequences may themselves contain other Sequences. The default execute( ) implementation loops over the members of the sequence, calling their execute( ) methods. However, this can be modified if a member is disabled, has already been executed, or a member indicates that it's filter fails. The the former two cases the execution of the member is bypassed. In the latter case, the loop is terminated and the Sequencer assumes the same filtered state as the last member.
Definition at line 24 of file Sequencer.h.
| Sequencer::Sequencer | ( | const std::string & | name, |
| ISvcLocator * | svcloc | ||
| ) |
Constructor(s)
Definition at line 22 of file Sequencer.cpp.
: Algorithm( name, pSvcLocator ), m_branchFilterPassed( false ) { // Create vector of branch algorithms m_branchAlgs = new std::vector<Algorithm*>(); // Declare Sequencer properties with their defaults declareProperty( "Members", m_names ); declareProperty( "BranchMembers", m_branchNames ); declareProperty( "StopOverride", m_stopOverride=false ); // Associate action handlers with the "Members" and "BranchMembers" properties m_names.declareUpdateHandler ( &Sequencer::membershipHandler , this ); m_branchNames.declareUpdateHandler( &Sequencer::branchMembershipHandler, this ); }
| Sequencer::~Sequencer | ( | ) | [virtual] |
| Sequencer::Sequencer | ( | const Sequencer & | a ) | [private] |
Private Copy constructor: NO COPY ALLOWED.
| StatusCode Sequencer::append | ( | Algorithm * | pAlgorithm ) |
Append an algorithm to the sequencer.
Definition at line 418 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = append( pAlgorithm, subAlgorithms( ) );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::append | ( | Algorithm * | pAlgorithm, |
| std::vector< Algorithm * > * | theAlgs | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Append an algorithm to the sequencer.
Protected Member Functions.
Definition at line 527 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
// Check that the specified algorithm doesn't already exist in the membership list
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( theAlgorithm == pAlgorithm ) {
result = StatusCode::FAILURE;
break;
}
}
if ( result.isSuccess( ) ) {
theAlgs->push_back( pAlgorithm );
pAlgorithm->addRef();
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::appendToBranch | ( | Algorithm * | pAlgorithm ) |
Append an algorithm to the sequencer branch.
Definition at line 425 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = append( pAlgorithm, branchAlgorithms( ) );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::beginRun | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Sequencer beginRun.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 269 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
// Bypass the loop if this sequencer is disabled
if ( isEnabled( ) ) {
// Loop over all members calling their sysInitialize functions
// if they are not disabled. Note that the Algoriithm::sysInitialize
// function protects this from affecting Algorithms that have already
// been initialized.
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgs = subAlgorithms( );
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
result = theAlgorithm->sysInitialize( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to initialize Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
break;
}
result = theAlgorithm->sysStart( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to start Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
break;
}
}
// Loop over all members calling their beginRun functions
// if they are not disabled.
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( ! theAlgorithm->isEnabled( ) ) {
theAlgorithm->beginRun( ).ignore();
}
}
// Loop over all branch members calling their sysInitialize functions
// if they are not disabled. Note that the Algoriithm::sysInitialize
// function protects this from affecting Algorithms that have already
// been initialized.
theAlgs = branchAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
result = theAlgorithm->sysInitialize( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to initialize Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
break;
}
result = theAlgorithm->sysStart( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to start Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
break;
}
}
// Loop over all branch members calling their beginRun functions
// if they are not disabled.
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( ! theAlgorithm->isEnabled( ) ) {
theAlgorithm->beginRun( ).ignore();
}
}
}
return StatusCode::SUCCESS;
}
| std::vector< Algorithm * > * Sequencer::branchAlgorithms | ( | ) | const |
List of branch algorithms.
These are the algorithms that would get executed if a filter algorithm indicated a failure. The branch is located within the main sequence by the first element, which is the filter algorithm.
Definition at line 480 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
return m_branchAlgs;
}
| bool Sequencer::branchFilterPassed | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Was the branch filter passed for the last event?
Definition at line 399 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
return m_branchFilterPassed;
}
| void Sequencer::branchMembershipHandler | ( | Property & | theProp ) |
"BranchMembers" property handler
Definition at line 517 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
if ( isInitialized() ) decodeBranchMemberNames();
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::createAndAppend | ( | const std::string & | type, |
| const std::string & | name, | ||
| Algorithm *& | pAlgorithm, | ||
| std::vector< Algorithm * > * | theAlgs | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Create a algorithm and append it to the sequencer.
A call to this method creates a child algorithm object. Note that the returned pointer is to Algorithm (as opposed to IAlgorithm), and thus the methods of IProperty are also available for the direct setting of the algorithm's properties. Using this mechanism instead of creating algorithms directly via the new operator is preferred since then the framework may take care of all of the necessary book-keeping.
Definition at line 549 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::FAILURE;
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
SmartIF<IAlgManager> theAlgMgr(serviceLocator()->service("ApplicationMgr"));
if ( theAlgMgr.isValid() ) {
IAlgorithm* tmp;
result = theAlgMgr->createAlgorithm( type, algName, tmp );
if ( result.isSuccess( ) ) {
try{
pAlgorithm = dynamic_cast<Algorithm*>(tmp);
theAlgs->push_back( pAlgorithm );
} catch(...){
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to create Algorithm " << algName << endmsg;
result = StatusCode::FAILURE;
}
}
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::createAndAppend | ( | const std::string & | type, |
| const std::string & | name, | ||
| Algorithm *& | pAlgorithm | ||
| ) |
Create a algorithm and append it to the sequencer.
A call to this method creates a child algorithm object. Note that the returned pointer is to Algorithm (as opposed to IAlgorithm), and thus the methods of IProperty are also available for the direct setting of the algorithm's properties. Using this mechanism instead of creating algorithms directly via the new operator is preferred since then the framework may take care of all of the necessary book-keeping.
Definition at line 432 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = createAndAppend( type, name, pAlgorithm, subAlgorithms( ) );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::createAndAppendToBranch | ( | const std::string & | type, |
| const std::string & | name, | ||
| Algorithm *& | pAlgorithm | ||
| ) |
Create a algorithm and append it to the sequencer branch.
A call to this method creates a child algorithm object. Note that the returned pointer is to Algorithm (as opposed to IAlgorithm), and thus the methods of IProperty are also available for the direct setting of the algorithm's properties. Using this mechanism instead of creating algorithms directly via the new operator is preferred since then the framework may take care of all of the necessary book-keeping.
Definition at line 441 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = createAndAppend( type, name, pAlgorithm, branchAlgorithms( ) );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::decodeBranchMemberNames | ( | ) |
Decode branch member name list.
Definition at line 504 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
// Decode the branch membership list
result = decodeNames( m_branchNames,
branchAlgorithms( ),
m_isBranchInverted );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::decodeMemberNames | ( | ) |
Decode Member Name list.
Definition at line 485 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
// Decode the membership list
result = decodeNames( m_names,
subAlgorithms( ),
m_isInverted );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::decodeNames | ( | StringArrayProperty & | theNames, |
| std::vector< Algorithm * > * | theAlgs, | ||
| std::vector< bool > & | theLogic | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Decode algorithm names, creating or appending algorithms as appropriate.
Definition at line 574 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result;
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
SmartIF<IAlgManager> theAlgMgr(serviceLocator()->service("ApplicationMgr"));
if ( theAlgMgr.isValid() ) {
// Clear the existing list of algorithms
theAlgs->clear( );
// Build the list of member algorithms from the contents of the
// theNames list.
const std::vector<std::string>& theNameVector = theNames.value( );
std::vector<std::string>::const_iterator it;
std::vector<std::string>::const_iterator itend = theNameVector.end( );
for (it = theNameVector.begin(); it != itend; it++) {
// Parse the name for a syntax of the form:
//
// <type>/<name>
//
// Where <name> is the algorithm instance name, and <type> is the
// algorithm class type (being a subclass of Algorithm).
const Gaudi::Utils::TypeNameString typeName(*it);
std::string theName = typeName.name();
std::string theType = typeName.type();
// Parse the name for a syntax of the form:
//
// <name>:invert
//
// Where <name> is the algorithm instance name and ":invert"
// indicates that the filter passed logic is inverted.
bool isInverted = false;
std::string::size_type invert = theName.find_first_of( ":" );
// Skip all occurrences of "::" (allow namespaces)
while ( std::string::npos != invert
&& invert < (theName.size() - 1) && theName[invert+1] == ':' )
invert = theName.find_first_of( ":", invert+2 );
if ( std::string::npos != invert ) {
if ( theName == theType ) {
// This means that we got something like "Type:invert",
// so we have to strip the ":invert" from the type too.
theType = theType.substr( 0, invert );
}
theName = theName.substr( 0, invert );
isInverted = true;
}
// Check whether the supplied name corresponds to an existing
// Algorithm object.
SmartIF<IAlgorithm>& theIAlg = theAlgMgr->algorithm(theName, false);
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = 0;
StatusCode status = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
if ( theIAlg.isValid() ) {
try{
theAlgorithm = dynamic_cast<Algorithm*>(theIAlg.get());
} catch(...){
log << MSG::WARNING << theName << " is not an Algorithm - Failed dynamic cast" << endmsg;
theAlgorithm = 0; // release
}
}
if ( theAlgorithm ) {
// The specified Algorithm already exists - just append it to the membership list.
status = append( theAlgorithm, theAlgs );
if ( status.isSuccess( ) ) {
ON_DEBUG log << MSG::DEBUG << theName << " already exists - appended to member list" << endmsg;
} else {
log << MSG::WARNING << theName << " already exists - append failed!!!" << endmsg;
result = StatusCode::FAILURE;
}
} else {
// The specified name doesn't exist - create a new object of the specified type
// and append it to the membership list.
status = createAndAppend( theType, theName, theAlgorithm, theAlgs );
if ( status.isSuccess( ) ) {
ON_DEBUG log << MSG::DEBUG << theName << " doesn't exist - created and appended to member list" << endmsg;
} else {
log << MSG::WARNING << theName << " doesn't exist - creation failed!!!" << endmsg;
result = StatusCode::FAILURE;
}
}
if ( status.isSuccess( ) ) {
theLogic.push_back( isInverted );
}
}
}
// Print membership list
if ( result.isSuccess() && theAlgs->size() != 0 ) {
log << MSG::INFO << "Member list: ";
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator ai = theAlgs->begin();
std::vector<bool>::iterator li = theLogic.begin();
for ( ; ai != theAlgs->end(); ++ai, ++li ) {
if ( ai != theAlgs->begin() ) log << ", ";
if ( (*ai)->name() == System::typeinfoName(typeid(**ai)) )
log << (*ai)->name();
else
log << System::typeinfoName(typeid(**ai)) << "/" << (*ai)->name();
if (*li) log << ":invert";
}
log << endmsg;
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::endRun | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Sequencer endRun.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 340 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
// Bypass the loop if this sequencer is disabled
if ( isEnabled( ) ) {
// Loop over all members calling their endRun functions
// if they are not disabled.
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgms = subAlgorithms( );
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend = theAlgms->end( );
for (it = theAlgms->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( ! theAlgorithm->isEnabled( ) ) {
theAlgorithm->endRun( ).ignore();
}
}
// Loop over all branch members calling their endRun functions
// if they are not disabled.
theAlgms = branchAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgms->end( );
for (it = theAlgms->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( ! theAlgorithm->isEnabled( ) ) {
theAlgorithm->endRun( ).ignore();
}
}
}
return StatusCode::SUCCESS;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::execute | ( | std::vector< Algorithm * > * | theAlgs, |
| std::vector< bool > & | theLogic, | ||
| Algorithm *& | lastAlgorithm, | ||
| unsigned int | first = 0 |
||
| ) | [protected] |
Execute the members in the specified list.
Definition at line 686 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
// Loop over all algorithms calling their execute functions if they
// are (a) not disabled, and (b) aren't already executed. Note that
// in the latter case the filter state is still examined. Terminate
// the loop if an algorithm indicates that it's filter didn't pass.
unsigned int size = theAlgs->size( );
for (unsigned int i = first; i < size; i++) {
lastAlgorithm = (*theAlgs)[i];
result = executeMember( lastAlgorithm );
if ( result.isSuccess( ) ) {
// Take the filter passed status of this algorithm as my own status.
// Note that we take into account inverted logic.
bool passed = lastAlgorithm->filterPassed( );
bool isInverted = theLogic[i];
if ( isInverted ) {
passed = ! passed;
}
setFilterPassed( passed );
// The behaviour when the filter fails depends on the StopOverride property.
// The default action is to stop processing, but this default can be
// overridden by setting the "StopOverride" property to true.
if ( ! isStopOverride( ) ) {
if ( ! passed ) break;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::execute | ( | ) | [virtual] |
The actions to be performed by the sequencer on an event.
This method is invoked once per event.
Definition at line 130 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
ON_DEBUG log << MSG::DEBUG << name( ) << " Sequencer::execute( )" << endmsg;
// Bypass the loop if this sequencer is disabled or has already been executed
if ( isEnabled( ) && ! isExecuted( ) ) {
Algorithm* lastAlgorithm;
result = execute( subAlgorithms( ), m_isInverted, lastAlgorithm );
if ( result.isSuccess( ) ) {
bool passed = filterPassed( );
if ( ! passed && ! isStopOverride( ) ) {
// Filter failed and stop override not set. Execute the
// branch if there is one associated with the filter
// algorithm that failed. Note that the first member on
// the branch is the failing algorithm and so should
// be skipped.
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgs = branchAlgorithms( );
if ( theAlgs->size( ) > 0 ) {
Algorithm* branchAlgorithm = (*theAlgs)[0];
if ( lastAlgorithm == branchAlgorithm ) {
// Branch specified - Loop over branch members
result = execute( branchAlgorithms( ),
m_isBranchInverted,
lastAlgorithm, 1 );
if ( result.isSuccess( ) ) {
// The final filter passed state will be set true if either
// of the main or branches passed, otherwise false.
// Save the branch filter passed state.
setBranchFilterPassed( filterPassed( ) ).ignore();
}
}
}
}
}
// Prevent multiple executions of this sequencer for the current event
setExecuted( true );
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::executeMember | ( | Algorithm * | theAlgorithm ) | [protected] |
Execute member algorithm.
Definition at line 726 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
if ( theAlgorithm->isEnabled( ) ) {
if ( ! theAlgorithm->isExecuted( ) ) {
result = theAlgorithm->sysExecute( );
// Set the executed state of the algorithm.
// I think this should be done by the algorithm itself, but just in case...
theAlgorithm->setExecuted( true );
}
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::finalize | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Sequencer finalization.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 179 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
// Loop over all branch members calling their finalize functions
// if they are not disabled. Note that the Algorithm::sysFinalize
// function already does this for the main members.
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgs = branchAlgorithms( );
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if (theAlgorithm->sysFinalize( ).isFailure()) {
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to finalize Algorithm "
<< theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
}
}
return StatusCode::SUCCESS;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::initialize | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Initialization of a sequencer.
Typically things like histogram creation, setting up of data structures etc, should be done here. If a sequence has properties specified in the job options file, they will be set to the requested values BEFORE the initialize() method is invoked.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 50 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgs;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend;
result = decodeMemberNames();
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to configure one or more sequencer members " << endmsg;
return result;
}
result = decodeBranchMemberNames();
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to configure one or more branch members " << endmsg;
return result;
}
// Loop over all sub-algorithms
theAlgs = subAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
result = theAlgorithm->sysInitialize( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to initialize Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
return result;
}
}
// Loop over all branches
theAlgs = branchAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
result = theAlgorithm->sysInitialize( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to initialize Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
| bool Sequencer::isStopOverride | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
Has the StopOverride mode been set?
Definition at line 412 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
return m_stopOverride.value( );
}
| void Sequencer::membershipHandler | ( | Property & | theProp ) |
"Members" property handler
Definition at line 498 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
if ( isInitialized() ) decodeMemberNames();
}
Private assignment operator: NO ASSIGNMENT ALLOWED.
| StatusCode Sequencer::reinitialize | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Sequencer Reinitialization.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 98 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
// Bypass the loop if this sequencer is disabled
if ( isEnabled( ) ) {
// Loop over all members calling their reinitialize functions
// if they are not disabled.
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgms = subAlgorithms( );
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend = theAlgms->end( );
for (it = theAlgms->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( ! theAlgorithm->isEnabled( ) ) {
theAlgorithm->reinitialize( ).ignore();
}
}
// Loop over all branch members calling their reinitialize functions
// if they are not disabled.
theAlgms = branchAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgms->end( );
for (it = theAlgms->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( ! theAlgorithm->isEnabled( ) ) {
theAlgorithm->reinitialize( ).ignore();
}
}
}
return StatusCode::SUCCESS;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::remove | ( | const std::string & | name ) |
Definition at line 458 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = remove( algname, subAlgorithms( ) );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::remove | ( | Algorithm * | pAlgorithm ) |
Remove the specified algorithm from the sequencer.
Definition at line 450 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
std::string theName = pAlgorithm->name( );
StatusCode result = remove( theName );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::remove | ( | const std::string & | algname, |
| std::vector< Algorithm * > * | theAlgs | ||
| ) | [protected] |
Remove the specified algorithm from the sequencer.
Definition at line 742 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
StatusCode result = StatusCode::FAILURE;
// Test that the algorithm exists in the member list
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if ( theAlgorithm->name( ) == algname ) {
// Algorithm with specified name exists in the algorithm list - remove it
// THIS ISN'T IMPLEMENTED YET!!!!
log << MSG::INFO <<"Sequencer::remove( ) isn't implemented yet!!!!!" << endmsg;
result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::removeFromBranch | ( | Algorithm * | pAlgorithm ) |
Definition at line 465 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
std::string theName = pAlgorithm->name( );
StatusCode result = removeFromBranch( theName );
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::removeFromBranch | ( | const std::string & | name ) |
Definition at line 473 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = remove( algname, branchAlgorithms( ) );
return result;
}
| void Sequencer::resetExecuted | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Reset the Sequencer executed state for the current event.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 371 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
Algorithm::resetExecuted( );
// Loop over all members calling their resetExecuted functions
// if they are not disabled.
std::vector<Algorithm*>* subAlgms = subAlgorithms( );
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend = subAlgms->end( );
for (it = subAlgms->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
theAlgorithm->resetExecuted( );
}
// Loop over all branch members calling their resetExecuted functions
// if they are not disabled.
subAlgms = branchAlgorithms( );
itend = subAlgms->end( );
for (it = subAlgms->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
theAlgorithm->resetExecuted( );
}
// Reset the branch filter passed flag
m_branchFilterPassed = false;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::setBranchFilterPassed | ( | bool | state ) | [virtual] |
Set the branch filter passed flag for the last event.
Definition at line 405 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
m_branchFilterPassed = state;
return StatusCode::SUCCESS;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::start | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Sequencer finalization.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 199 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
StatusCode result = StatusCode::SUCCESS;
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgs;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend;
// Loop over all sub-algorithms
theAlgs = subAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
result = theAlgorithm->sysStart( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to start Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
return result;
}
}
// Loop over all branches
theAlgs = branchAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
result = theAlgorithm->sysStart( );
if( result.isFailure() ) {
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to start Algorithm " << theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
| StatusCode Sequencer::stop | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Sequencer finalization.
Reimplemented from Algorithm.
Definition at line 236 of file Sequencer.cpp.
{
// Loop over all branch members calling their finalize functions
// if they are not disabled.
std::vector<Algorithm*>* theAlgs;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator it;
std::vector<Algorithm*>::iterator itend;
theAlgs = subAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if (theAlgorithm->sysStop( ).isFailure()) {
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to stop Algorithm "
<< theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
}
}
theAlgs = branchAlgorithms( );
itend = theAlgs->end( );
for (it = theAlgs->begin(); it != itend; it++) {
Algorithm* theAlgorithm = (*it);
if (theAlgorithm->sysStop( ).isFailure()) {
MsgStream log( msgSvc( ), name( ) );
log << MSG::ERROR << "Unable to stop Algorithm "
<< theAlgorithm->name() << endmsg;
}
}
return StatusCode::SUCCESS;
}
std::vector<Algorithm*>* Sequencer::m_branchAlgs [private] |
Definition at line 247 of file Sequencer.h.
bool Sequencer::m_branchFilterPassed [private] |
Definition at line 250 of file Sequencer.h.
StringArrayProperty Sequencer::m_branchNames [private] |
Definition at line 246 of file Sequencer.h.
std::vector<bool> Sequencer::m_isBranchInverted [private] |
Definition at line 248 of file Sequencer.h.
std::vector<bool> Sequencer::m_isInverted [private] |
Definition at line 245 of file Sequencer.h.
StringArrayProperty Sequencer::m_names [private] |
Definition at line 244 of file Sequencer.h.
BooleanProperty Sequencer::m_stopOverride [private] |
Definition at line 249 of file Sequencer.h.